How to Read Data with JSON-RPC
We use JSON-RPC to communicate with Ethereum. All nodes have a JSON-RPC interface for read requests. Signed JSON-RPC requests are needed for writing.
Previous Section Recap
In the previous section, we learned that **[Ethereum is simply a computer]()**. This computer has the following properties:
- Censorship Resistance: programs (aka: smart contracts) on the Ethereum computer are permanent executables - except in the case where the program explicitly is built with a path to call
selfdestruct() - Ubiquitous: where there is Internet, there is Ethereum.
- Cryptographic assurances for data permanence, integrity, & verifiability
In the Ethereum computer, there are only two types of accounts that can have a public address:
- EOAs (Externally Owned Accounts): accounts that own a private key, typically humans but can be bots set up by humans too
- Smart Contracts: don't own a private key, are only triggered by being called by an EOA first
How to read Ethereum data?
Ethereum is simply a computer for all intents and purposes. The main difference is that this single computer is spread out over thousands of nodes worldwide. The Ethereum computer is built in such a way that it does not matter which of these nodes you communicate with, you are ultimately only affecting one single instance: the Ethereum world state trie singleton.
Conceptually, that's all fine and well. But how do we actually communicate with the Ethereum computer? The answer is: JSON-RPC.
What We Are Ultimately Trying To Build

The above image is a super simplified view of what we will learn today: JSON-RPC is the bridge we use to connect any dApp we use/build to an Ethereum node, and thus the greater Ethereum network.
Keep this diagram in mind as we further learn about communicating data via JSON-RPC! 🧠
Core Concept: Ethereum Clients
To run an Ethereum node, you must run one of the various Ethereum client implementations. You will see, there are quite a few including:
- geth: Ethereum client written in Go
- erigon: Ethereum client also written in Go
- nethermind: Ethereum client written in .NET
Here is some more information on Ethereum nodes and clients.
The main takeaway at this point is: in order to run a node, you must download, install and run an Ethereum client implementation. These Ethereum clients use JSON-RPC, and thus define methods like eth_getBlockByNumber that is by default queryable by any JSON-RPC compatible Request. More below...
Core Concept: JSON-RPC
JSON-RPC is a remote procedure call (RPC) protocol that uses JSON to encode messages. In other words, JSON-RPC is simply another API standard.
JSON-RPC is a similar API standard to REST, typically considered useful for CRUD.
JSON-RPC deals exclusively with transporting data in the syntax form of JSON. RPC (remote procedure call) on the right-hand side of the term simply gives us more clues that this is a communication protocol. Whenever you see "RPC", think: "There is a server out there and I want to call a method on it by executing a remote procedure call".
All Ethereum nodes contain a JSON-RPC interface. This means that some of the following methods are directly queryable to an Ethereum node:
eth_blockNumbereth_getBalanceeth_getBlockByNumbereth_sendRawTransaction(covered in the next module)
Here's a fuller documentation of all the methods that are contained in the Ethereum JSON-RPC interface, ready to be pinged at any moment by the dApps we will build!
Visualization of API Standards: REST and JSON-RPC
REST is a very popular API standard. If you've ever worked with databases and record-keeping, chances are you've used the REST API standard. This is what that flow looks like:
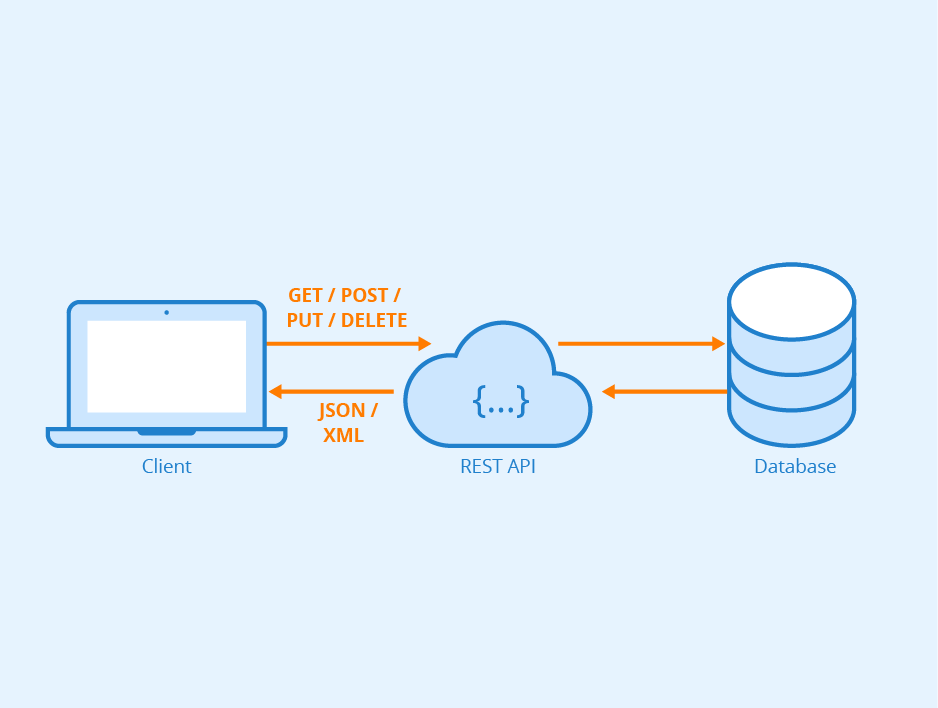
REST flow:
- You have some client application (i.e., Twitter)
- The client application sends a request, for example:
DELETE_TWEET - The database, loaded with a REST API standard interface, accepts the request, updates the resource (deletes a tweet), and sends back a response, either success or fail.
JSON-RPC is a very similar flow, in the sense that you are sending Requests and getting back Responses to a server - in our case, an Ethereum node acting as a listening server!

JSON-RPC flow:
- On the client side, formulate a JSON-RPC request. Typically, this would be you or a user clicking a button that initiates some action to the Ethereum computer, for example, a button that is rigged to make a
eth_blockNumberrequest to the provider - Your web3 wallet, acting as a provider, will route the
Requestto the Ethereum node it is connected to - The Ethereum node will receive the
Request, run theeth_blockNumbermethod in the request and send back aResponsecontaining the latest block # on Ethereum
Remember,
provideris just a fancy term for something representing a connection to an Ethereum node!
JSON-RPC Request

The above is what a JSON-RPC Request that asks for the account balance of an address looks like. It specifies:
- The
jsonrpcversion, which is always2.0 - The specific
methodthat you would like to call (must be a method in the interface!) - Any
paramsrelevant to themethodcalled - The
idof the request is any arbitrary number you choose. Theidproperty is only relevant when you are batching requests, if you are making stand-alone requests you can just use0.
JSON-RPC Response

The above is what a JSON-RPC Response looks like, in particular, the response to the eth_getBalance request made above.
The Response contains:
- The
jsonrpcversion just mirrored back, always2.0 - The
resultof theeth_getBalancequery, in this case0x7cf7d42bb6a906, which is the hexadecimal representation of35175387750639880 weiwhich is simply0.03517538775063988 ETHworth of an account balance 💯
We used this converter: https://www.alchemy.com/gwei-calculator to convert from
weitoether.
- The
idof the single request
JSON-RPC Tools
Try using the Alchemy Composer to make JSON-RPC requests in an instant! Try a few different methods!
Suggested Reading
🏁 Conclusion
Thanks to every Ethereum node containing a JSON-RPC interface, we can communicate with the Ethereum blockchain in an instant. We can make important READ requests like eth_getBlockByNumber and eth_getBalance to the Ethereum blockchain at any time.
In this section, we learned how to manage basic read requests from Ethereum. What if we want to write to the Ethereum computer? As in, actually, make a change of state! Anyone can ask for information at any time (did you try the Alchemy Composer?), but what about requests to write information to Ethereum? These write requests can be contract interactions or even a simple Ethereum transfer. The next section covers signed JSON-RPC requests, in other words: transactions.
Learn More About Ethereum Development
Alchemy University offers free web3 development bootcamps that explain Ethereum in-depth and help developers master the fundamentals of web3 technology. Sign up for free, and start building today!
Updated almost 2 years ago
